|
 Home
> General Information
> Economy and Government Home
> General Information
> Economy and Government
Introduction | Facts |
Travel Essentials |
Geography and Climate |
Language
Culture and Religion | Economy and
Government |
Night Life |
Sports
The Lebanese economy was completely destroyed during the 15-year civil war from 1976 to 1991.
Beirut’s position as a major financial
and commercial centre for the Middle East was lost. Since the end of the war, both Lebanon
and Beirut have gone a long way to re-establishing themselves.
During the civil war, agriculture sustained the population with citrus fruit, olives and cereals as the main products. Light
industries include textiles, processed foods and industrial machinery. There
are no significant mineral resources in Lebanon, but the manufacturing industry is growing
rapidly. In the all-important service sector, the two main components,
Banking and Transit Trade have recovered reasonably well.
Essential reconstruction, financed by expatriate capital, international aid and
foreign investment, began with infrastructure projects. A variety of
programmes were consolidated in the ‘Horizon 2000’ under which,
beginning in 1993, the Government committed to spending an estimated US$20
billion on reconstruction. However, by the late 1990s, the Government’s
failure to control the budget deficit and external debt was causing serious
difficulties.
|
Moreover, Lebanon is critically affected by the
political developments in the Middle-East region. At the end of 2000, the Government
introduced a major reform programme based on privatisation and promotion of
foreign investment. This appears to be paying dividends and, in 2002, it was
supplemented by a major bilateral trade deal with the EU. Besides the EU, Saudi
Arabia, Syria, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait are Lebanon’s principal
trading partners.
Lebanon is a democratic republic with a
parliamentary system of government and a cabinet headed by a Prime Minister.
Its constitution is based on the separation of executive, legislative and
judicial powers, with a president elected every 6 years. 128 Members of
Parliament are elected by universal adult sufferage for a four year term. 50%
should be Muslims, and 50% Christians. Traditionally the president of Lebanon
comes from the Christian Maronite community and the prime minister from the
Muslim Sunnite community.
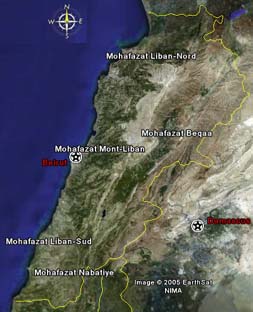
The Lebanese
Republic is divided into six regional governments, or Mohafazaat: Beirut, North
Lebanon, Mount Lebanon, South Lebanon, The Bekaa Valley and Nabatiyeh.
|
|
 |
Introduction | Facts |
Travel Essentials |
Geography and Climate |
Language
Culture and Religion | Economy and
Government |
Night Life |
Sports
|









